Workplace Hazards are dangerous conditions
Workplace hazards are either potential or inherent, which can interfere with the expected, orderly progress of a given activity.
Workplace Hazard Assessment Risk: A measured or calculated chance of exposure to hazard(s) that may or may not result in loss.
 Both workplace hazards and risks should be managed
Both workplace hazards and risks should be managed
Where to look for workplace hazards:
Machines, lifting equipment, facility design, confined spaces, fire considerations, biological, ergonomic, energy, chemical, pressure vessels, electrical.
Workplace Hazard Reduction Measures:
Design feature, safety device or feature, warning device, procedure and training. It may take some serious thinking before the best approach is determined.
You must assess the risk of hazard exposure and determine the pratical methods to best eliminate or reduce that risk to the lowest possible or acceptable levels.
System Safety Criteria:
Workplace Hazard Severity (“qualitative” assessment “):
– A categorical description of the hazard level
– Based on real/perceived potential for causing harm/damage
Hazard probability (“quantitative” assessment “):
– The calculated likelihood that a condition(s) will exist.
What do you do if a risk is unacceptable?
1. Design feature
2. Safety device
3. Warning devices
4. Procedures and training
Personal protective equipment (PPE) for the eyes and face is designed to prevent or lessen the severity of injuries to workers. The employer must assess the workplace and determine if hazards that necessitate the use of eye and face protection are present or are likely to be present before assigning PPE to workers.
A hazard assessment should determine the risk of exposure to eye and face hazards, including those that may be encountered in an emergency. Employers should be aware of the possibility of multiple and simultaneous hazard exposures and be prepared to protect against the highest level of each hazard.
Impact Hazards:
The majority of impact injuries result from flying or falling objects or sparks striking the eye. Most of these objects are smaller than a pin head and can cause serious injury such as punctures, abrasions, and contusions.
While working in a hazardous area where the worker is exposed to flying objects, fragments, and particles, primary protective devices such as safety spectacles with side shields or goggles must be worn. Secondary protective devices such as face shields are required in conjunction with primary protective devices during severe exposure to impact hazards.
Heat injuries:
These may occur to the eye and face when workers are exposed to high temperatures, splashes of molten metal, or hot sparks. Protect your eyes from heat when workplace operations involve pouring, casting, hot dipping, furnace operations, and other similar activities. Burns to the eye and face tissue are the main concern when working with heat hazards.
Working with heat hazards requires eye protection such as goggles or safety spectacles with special-purpose lenses and side shields. However, many heat hazard exposures require the use of a face shield in addition to safety spectacles or goggles. When selecting PPE, consider the source and intensity of the heat and the type of splashes that may occur in the workplace.
Chemicals:
A large percentage of eye injuries are caused by direct contact with chemicals. These injuries often result from an inappropriate choice of PPE, that allows a chemical substance to enter from around or under protective eye equipment. Serious and irreversible damage can occur when chemical substances contact the eyes in the form of splash, mists, vapors, or fumes. When working with or around chemicals, it is important to know the location of emergency eye wash stations and how to access them with restricted vision.
When fitted and worn correctly, goggles protect your eyes from hazardous substances. A face shield may be required in areas where workers are exposed to severe chemical hazards.
Dust:
Dust is present in the workplace during operations such as woodworking and buffing. Working in a dusty environment can cause eye injuries and presents additional hazards to contact lens wearers.
Either eyecup or cover-type safety goggles should be worn when dust is present. Safety goggles are the only effective type of eye protection from nuisance dust because they create a protective seal around the eyes.
Optical Radiation:
Laser work and similar operations create intense concentrations of heat, ultraviolet, infrared, and reflected light radiation. A laser beam, of sufficient power, can produce intensities greater than those experienced when looking directly at the sun.
Unprotected laser exposure may result in eye injuries including retinal burns, cataracts, and permanent blindness. When lasers produce invisible ultraviolet or other radiation, both employees and visitors should use appropriate eye protection at all times.
Determine the maximum power density or intensity, lasers produce when workers are exposed to laser beams. Based on this knowledge, select lenses that protect against the maximum intensity. The selection of laser protection should depend upon the lasers in use and the operating conditions. Workers with exposure to laser beams must be furnished with suitable laser protection.
Workplace Hazard Assessment
Workplace Hazard type
Workplace Hazard Safety – Examples of Hazard Common Related Tasks Impact
Flying objects – such as large chips, fragments, particles, sand, and dirt. Chipping, grinding, machining, masonry work, woodworking, sawing, drilling, chiseling, powered fastening, riveting, and sanding.
Heat – Anything emitting extreme heat. Furnace operations, pouring, casting, hot dipping, and welding.
Chemicals – Splash, fumes, vapors, and irritating mists. Acid and chemical handling, degreasing, plating, and working with blood.
Other Workplace Hazards include:
Dust – Harmful Dust. Woodworking, buffing, and general dusty conditions.
Optical Radiation – Radiant energy, glare, and intense light.
Welding, torch-cutting, brazing, soldering, and laser work.
When specifying emergency shower and eye wash equipment you should refer to the American National Standard ANSI Z358.1 2014 “Emergency Eye Wash and Shower Equipment”.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Labor. Congress established the agency under the Occupational Safety and Health Act,

 The Comfortcool™ Principle:
The Comfortcool™ Principle:
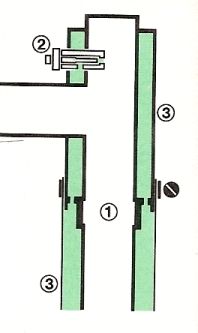 The supply of water is held static in the supply tube (1). A needle valve (2) allows water from the supply tube to enter the jacket (3) from which it percolates to the outside surface and evaporates to the atmosphere. This avoids wastage of water when, to maintain cool conditions, it is allowed to trickle from the system or discharge regularly under temperature control. Also, this overcomes the dangerous and avoidable time delay encountered when dry pipe showers are employed.
The supply of water is held static in the supply tube (1). A needle valve (2) allows water from the supply tube to enter the jacket (3) from which it percolates to the outside surface and evaporates to the atmosphere. This avoids wastage of water when, to maintain cool conditions, it is allowed to trickle from the system or discharge regularly under temperature control. Also, this overcomes the dangerous and avoidable time delay encountered when dry pipe showers are employed.








